Asymmetric catalysis is one of the most active branches in modern organic chemistry research, and asymmetric catalytic reactions are considered to be the most efficient methods for synthesizing chiral substances. The principle is to convert achiral raw materials into chiral products by using chiral catalysts. Therefore, the chiral ligand complexed...
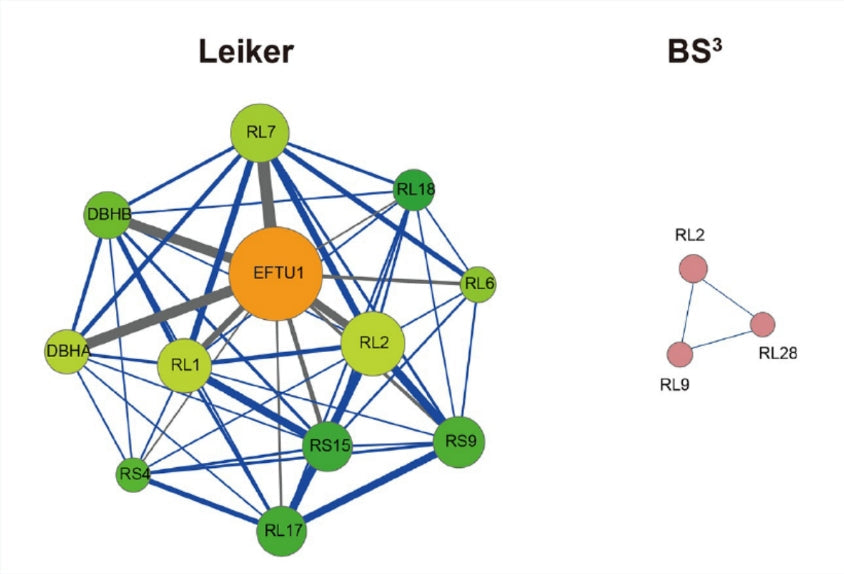
Chemical cross-linking coupled with mass spectrometry (CXMS) has been booming in the past decade and is widely used in protein structure identification and protein interaction analysis. However, the chemical cross-linking agents available for CXMS technology are limited and the cross-linking efficiency is not high enough, which limits the application of...
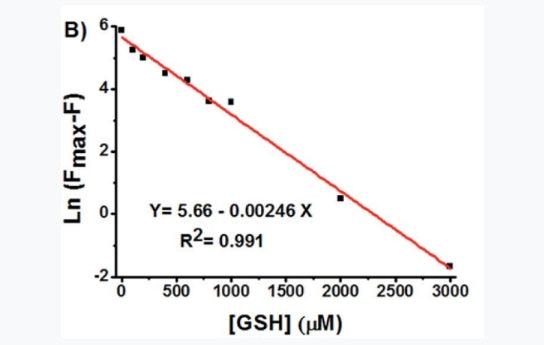
Chemotherapy is currently the main means of treating cancer, but tumor cells may develop drug resistance, and the mechanism is complex. High levels of reduced glutathione (GSH) may be an important reason for this phenomenon. To reveal the detailed role of GSH in chemoresistance, it is crucial to find a...
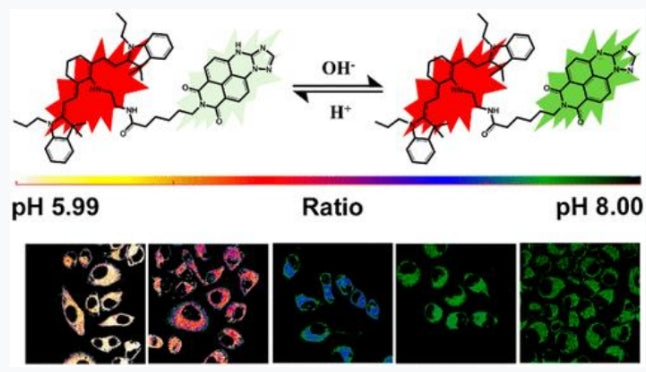
Changes in intracellular and intracellular pH play an important role in physiological and pathological processes. Changes in intracellular pH can easily induce cell division, rapid growth and functional disorders. The reduction of extracellular pH to acidic is an important signal for cancer and other lesions. Therefore, the detection of pH...
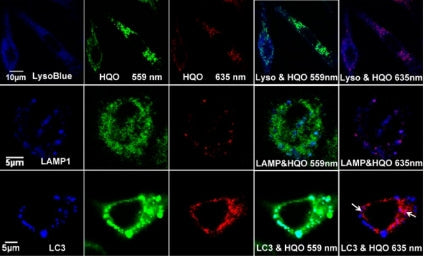
Mitophagy is the process by which cells remove damaged or aged mitochondria and recycle their constituent elements. It is closely related to many physiological and pathological processes such as aging, neurodegenerative diseases, and cancer, so the study of mitophagy is of great significance.Currently, two methods are mainly used to study...

Nitrogen-containing compounds widely exist in natural products, drugs, functional materials and other fields, so the efficient construction of C-N bonds has attracted much attention. Traditionally, the formation of amide groups mainly relies on the homocleavage of N-X bonds, but N-X bonds are difficult to construct under harsh conditions, which fundamentally...

